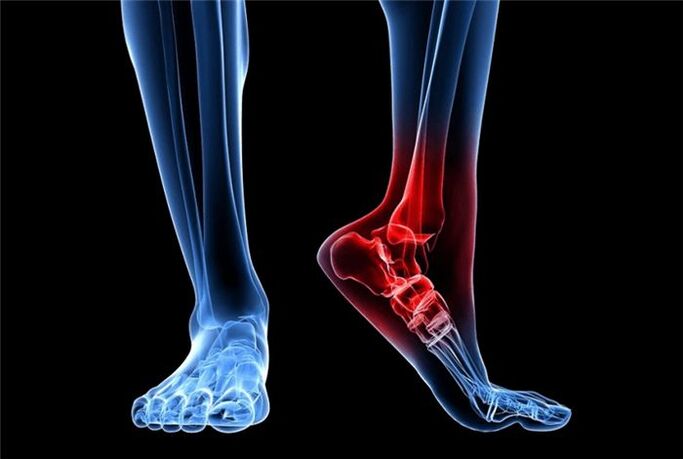
Arthrosis of the joints is a chronic joint disease that develops due to metabolic disorders. As a result, degenerative, dystrophic changes and destruction of cartilage tissue occur.
It occurs imperceptibly, but often develops very quickly. A person begins to feel pain in the joints when moving, there is stiffness and reduced mobility, especially in the morning, while still "not in contrast". If discomfort appears and periodic pain occurs during awkward movements or loads, it is very important to understand that this will not go away and without intervention the situation will get worse.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
Arthrosis of large and medium joints seriously changes a person's lifestyle, worsens the quality and imposes restrictions. The development of the disease is like an avalanche, and treatment is often associated with unbearable pain, and this is a clear sign of wear on the joints.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the joints depend on how much the joint, cartilage and nearby tissues are affected.
In the initial stages, osteoarthritis can be determined quite accurately, the treatment in this case is sparing and does not require serious intervention and expensive drugs for the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Types of osteoarthritis
Arthrosis of the joints is classified according to several criteria. Depending on the degree of arthrotic changes in the cartilage tissue, 4 stages of arthrosis are distinguished. Osteoarthritis is also divided into primary and secondary. The cause of the development of primary osteoarthritis is age-related changes. Secondary osteoarthritis occurs due to injuries and diseases of the joints (for example, traumatic osteoarthritis or rheumatoid osteoarthritis). The disease can also develop slowly over the years or lead to joint destruction over a few years (progressive osteoarthritis).
There is alsotypes of osteoarthritis depending on the affected area:
- - arthrosis of the knee joint - arthrosis of the hip joint
- Non-vertebral arthrosis - arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae
- Vertebral arthrosis - damage to the spine
- Patellofemoral arthrosis is a type of gonarthrosis in which the patella and part of the femur suffer.
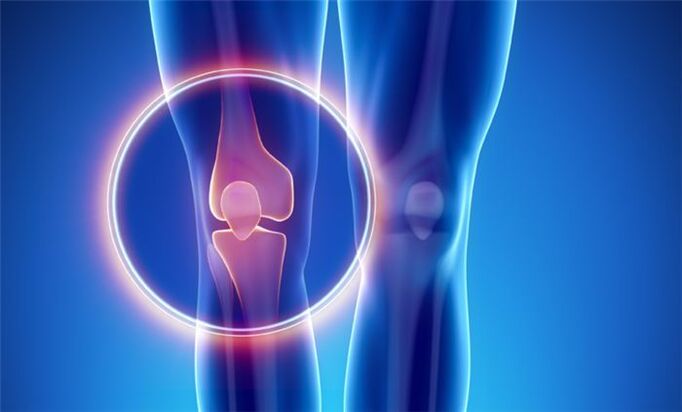
The degree of disease is determined by the degree of tissue damage of the cartilage.
1st degree arthrosis: the cartilage tissue is slightly damaged, the person does not feel uncomfortable;
Arthrosis II degree - osteophytes appear, the space between the cartilages decreases, situational pain occurs with awkward movements;
III degree arthrosis: cartilage tissue is destroyed in some places and exposes bone tissue, the space between cartilages decreases, pain is frequent and severe;
Arthrosis of IV degree - a significant part of the cartilage tissue is destroyed up to 60%, there is no space between the bones, patients experience constant and intense pain, hyperthermia of the area above the joint occurs.
- A characteristic crunch during movements and a slight aching background pain;
- Limitation of joint mobility, discomfort during full physical activity;
- "Jumping" blood pressure indicators;
- Headache and dizziness;
- Seizure syndrome and often muscle spasms;
- Visually observed deformity of the joint;
- Swelling, hyperthermia, or redness of the skin area above the diseased joint
- Violation of motor function.
Why does the disease appear
Osteoarthritis of the joints can occur in any ward, but very often patients turn around when osteoarthritis of the knee or hip joint makes itself felt. In the professional environment, with a special and specific load on the hands, osteoarthritis of the shoulder can be observed.
Injuries differ in men and women.The strong half often suffers from temporomandibular, wrist, ankle and lumbar arthrosis. Women complain most of the thoracic and cervical regions, as well as the joints of the fingers and toes.
The type of disease is determined by the location of the lesion. There are the following types:
- arthrosis of the hip joint - coxarthrosis;
- arthrosis of the knee joint - gonarthrosis;
- damage to the patella and part of the femur - patellofemoral arthrosis (a type of gonarthrosis);
- spine disease - vertebral arthrosis;
- damage to the cervical spine - non-vertebral arthrosis.
The main reasons are:
- inflammatory process;
- professional sports;
- overweight;
- non-standard professional load, for example, squatting or kneeling;
- previous joint injuries (post-traumatic);
- hypothermia;
- inheritance;
- age changes.
Osteoarthritis can appear as an independent disease or it can be the result of a disease already in progress, so it is important to know a person's history.
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the joints
Osteoarthritis of the joints is detected by X-rays. The X-ray image shows how the joint is deformed and how much the joint space narrows. It may also be necessary to undergo an MRI or arthroscopy, but only in particularly complex and ambiguous cases. X-rays of the joints are usually sufficient to diagnose the disease.
To understand the presence of the disease, its severity and what ailments led to the disease, a comprehensive diagnosis is performed.
First, with the helpradiography in different projectionsreceive information on the degree of damage to the joint.
Tomography (magnetic or computed resonance imaging) helpsexclude tumor processes.
Third, you needto practiceunderstand whether osteoarthritis is an independent disease or complication, as well as determine the general condition of a person.
The complex of studies is the most informative and gives a clear idea of the degenerative-dystrophic changes and helps to choose the optimal treatment plan.
Treatment of arthrosis
As discussed above, osteoarthritis can develop due to many factors, and the treatment plan is developed based on understanding the underlying causes, and osteoarthritis treatment medications are selected accordingly.
Treatment must be developed individually, based on the results of the diagnosis. Be sure to take into account the condition of the person, his existing diseases.
The restoration of the joint surface and cartilage tissue is not quick. Effective drugs are prescribed that have side effects. And taking medication to achieve the desired result lasts up to 6 months, so it is important to protect your health as much as possible from side effects.
Medical treatment of osteoarthritis
The main goal of such therapy is to remove the manifestations of arthrosis. Pharmacological treatment of arthrosis of the joints includes:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories. With osteoarthritis, a person experiences pain, the joint becomes inflamed. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms and stop inflammation, this group of drugs is prescribed.
- Hormonal injections into the joint. Corticosteroid drugs are most often administered in the acute phase of osteoarthritis.
- Chondroprotectors. The main task of these drugs is to stop the degenerative processes in the cartilage tissue to prevent its further destruction.
- Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic acid preparations are similar to synovial fluid, which provides smooth and fluid movements in the joint. With osteoarthritis, synovial fluid is not secreted sufficiently, so orthopedists often prescribe hyaluronic acid injections (injections into the joint with osteoarthritis).
- Biological therapy of arthrosis (PRP and cytokine therapy). An innovative new method of osteoarthritis therapy, which has recently come into practice, but which is gaining popularity. This is the use of drugs based on the patient's blood plasma enriched with platelets. Thanks to biological therapy, the blood supply to the joint is activated, the production of intra-articular fluid is activated and the cartilage tissue is supplied with nutrients.
Important!Drug treatment of arthrosis is effective in the early stages of the disease. In addition, experts point out that drug therapy is not able to restore a damaged joint, but will allow to eliminate symptoms and slow the progression of arthrosis.
Physiotherapy and other conservative treatments for osteoarthritis
Physiotherapy is also used in the fight against osteoarthritis. Various procedures are prescribed (laser, phonophoresis, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, UVT) and physical therapy to improve metabolic processes and blood circulation, strengthen muscles.
Also, with osteoarthritis, you just need to make a few changes to your lifestyle:
- Avoid Overloading: It is important to evenly distribute the activity and take breaks so as not to overload the joint
- Take care of your nutrition and control your weight - since being overweight only aggravates the joint problem, it is necessary to review the diet and reduce body weight
- Remember to be careful and avoid injuries as much as possible
- Use additional support for movement: In the later stages of osteoarthritis, independent movement becomes questionable, so you need to use a cane or crutches. For a more comfortable walk, you can also use orthopedic insoles - they will reduce the load on the joint.
There are also many popular recipes that "will help defeat osteoarthritis". However, even the treatment of osteoarthritis at home does not always bring results. In addition, the use of all kinds of lotions and ointments of their own preparation very often causes only allergic reactions and does not affect the health of the joint.
Surgical treatment of osteoarthritis
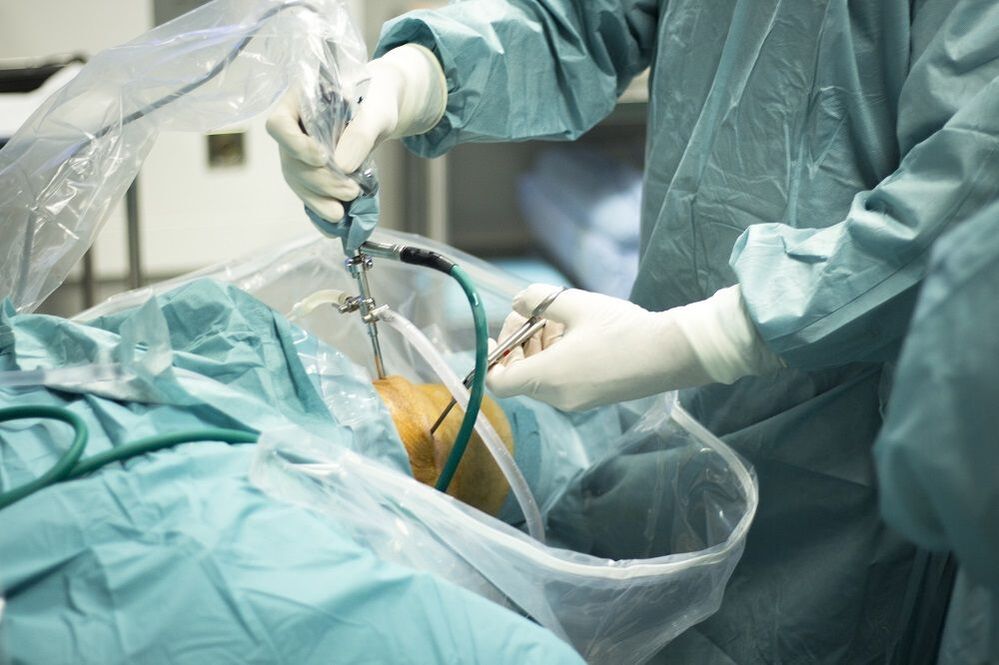
How to treat osteoarthritis if all of the above methods do not work? In this case, surgical treatment of osteoarthritis is prescribed. Depending on the degree of damage to the joint, the individual characteristics of each patient, a type of operation is selected.
Joint arthroscopy is a low-traumatic operation, an intra-articular operation through several micro perforations in the joint. With osteoarthritis, it is used as a temporary measure to "clean the joint": removing parts of cartilage, osteophytic growths that interfere with free circulation. This treatment reduces joint pain, but it is not a solution to the problem of osteoarthritis.
Osteotomy is an operation to align the axis of the joint. The fact is that with osteoarthritis, as a rule, part of the joint suffers the most (it has a large load). As a result of the osteotomy, the load on the joint is redistributed. It should be noted that osteoarthritis is a progressive disease of the joints. Therefore, osteotomy is a way to delay further treatment, but not to avoid it.
Joint arthroplasty is an effective and in some cases the only method for treating osteoarthritis of the joints. The essence of the operation is the removal of a joint destroyed by the disease and the implantation of an artificial endoprosthesis in its place. The artificial joint is selected individually, perfectly suited to each patient and fully restores the functions of the damaged joint after a rehabilitation period.
Contraindications for osteoarthritis
What you need to pay attention to in arthrosis of the joints:
Joint loads- with osteoarthritis, it is necessary to abandon weight lifting, excessive static loads. A barrel can be used to unload the joint. Shoes - Properly fitted shoes reduce stress on the joint. It is advisable to avoid high-heeled shoes.
Weight- overweight is another factor in the progression of osteoarthritis. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy weight and eat a balanced diet.
Sportsalso to be reviewed. With arthrosis, it is necessary to exclude sharp and jerky movements (contact sports, wrestling), running long distances, lifting weights. But this does not mean that physical activity should be stopped altogether. Moderate activity will only benefit the joint.
In addition to medical treatment, physiotherapy is actively used. These are magnetotherapy, electrotherapy, thermotherapy. Additionally, physiotherapy exercises are recommended to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint and improve blood supply.
A radical method of deforming osteoarthritis, which has led to a deterioration in the quality of life, is often surgery. In this case, arthroscopy or arthroplasty is performed.
Arthroscopy is a procedure in which the worn top layer of a joint is removed and a partial denture is placed in its place. This allows you to get rid of pain and restore mobility.
Endoprosthesis is the replacement of a joint with a prosthesis. It is appropriate for severe destruction, when the joint itself makes no sense to save. The prosthesis has artificial cartilage, which anatomically corresponds perfectly to the human one.
Treatment of the disease in the initial stage is the provision of high-quality nutrition for the cartilage tissue. For this purpose, the use of chondroprotectors, preferably of natural origin, flavonoids is recommended. Motor load is also needed to improve blood supply to the bones and perichondrium.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee
Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint(gonarthrosis, DAK) is a chronic progressive disease of the articular cartilage. It is characterized by the destruction of joint structures, which is accompanied by pain, inflammation and a characteristic curvature of the limb ("legs with wheel" or X-shaped deformation).
Causes of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee
Without proper lubrication, the joint "dries up", cracks and loses height, exposing the heads of the bones. In this case, the closure plate of the articular surface of the bone remains defenseless; re-irritation of the numerous nerve endings found there causes pain and discomfort.
The following factors or their combination can become the cause of knee osteoarthritis deformation:
- the presence of diseases of the joints (and knee - in particular) in relatives;
- genetic disorders associated with the formation of abnormal and unstable cartilage cells or their accelerated death;
- congenital and acquired malformations of the musculoskeletal system (flat feet, joint hypermobility, dysplasia, scoliosis, kyphosis and others);
- excessive professional, domestic or sports loads;
- microtrauma and injuries of the knee joint and meniscus, operations on it, leg fractures;
- circulatory disorders (varicose veins, atherosclerosis, thrombosis and other vascular diseases), their consequences (osteochondritis dissecans), as well as other causes of prolonged spasms in the legs;
- inflammatory diseases of the joints and periarticular tissues (synovitis, bursitis, tendonitis, arthritis), incl. autoimmune nature (rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis);
- metabolic disorders (gout, diabetes mellitus);
- age-related processes of aging of the joints and leaching of calcium from the bones;
- hormonal disruptions and changes in the hormonal background (for example, associated with a lack of estrogen in women);
- hypovitaminosis;
- excess weight (observed in ⅔ of patients);
- physical inactivity.
But the main reason deforming knee osteoarthritis is so common lies in its structure. The knee joint has only one axis (plane) of motion. Therefore, the range of permitted movements is very limited. An awkward turn can injure periarticular tissues and trigger arthritic changes - after all, the sore knee will be under daily stress.
The causes of the development of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee can be a large number of factors.

Symptoms of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Gradually increasing pain in the knee joint area. In the beginning, the pain is noticeable only when moving - for example, with a strong straightening or bending of the leg, one has the feeling that "sadly you are stepping on your foot". In the early stages, the pain may be episodic or so mild that it is perceived as discomfort. Then the pain intensifies after physical exertion or a long stay in the same position. The skin also becomes painful: it reacts sensitively to any touch, incl. and clothes.
There are 3 types of pain specific to the deformation of osteoarthritis of the knee joint:
- departure (lasts 15-30 minutes after the joint has come out of a long state of rest);
- mechanical (perceptible during physical activity and disappears after rest);
- blockage (sensation of a strong pinching in the knee).
Symptoms of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee, as a rule, grow slowly due to the fact that the disease is not characterized by rapid progress. This is the insidiousness of arthrosis: gradually getting used to the discomfort of the disease, the patient "gets used" to the pain, does not notice the deterioration and postpones the visit to the doctor.
Knowing the main symptoms of deforming knee osteoarthritis will help to recognize the disease in time
Treatment of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Treatment of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint consists in the complex use of drugs, a dosed load on the joint, physiotherapy procedures and the use of orthopedic devices.
In the treatment process, it is extremely important to alternate loading and unloading, to prevent static loading of the knee. Orthopedic insoles, specialized shoes, canes, crutches, walkers, ergonomic chairs for work and rest also help slow the disease. Particularly effective are orthoses with variable stiffening, which allow you to model the physiological axis of the leg and compensate for the deformity.
In the early stages of deforming knee osteoarthritis, the goal of treatment is to restore the destroyed joint and ligament apparatus, relieve pain and increase the range of voluntary movement. In the second - in relieving the patient's condition. For this, sanatorium arthroscopy (washing with antiseptics) is performed when a piece of osteophyte is broken, corrective osteotomy (correction of a curved bone), endoprosthesis (replacement) of the joint.
In addition to the orthopedist, physiotherapists and chiropractors, physical therapy and therapeutic massage specialists and surgeons will tell you how to treat deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
The treatment of deforming osteoarthritis of the joints is a complex and lengthy process that requires an integrated approach.
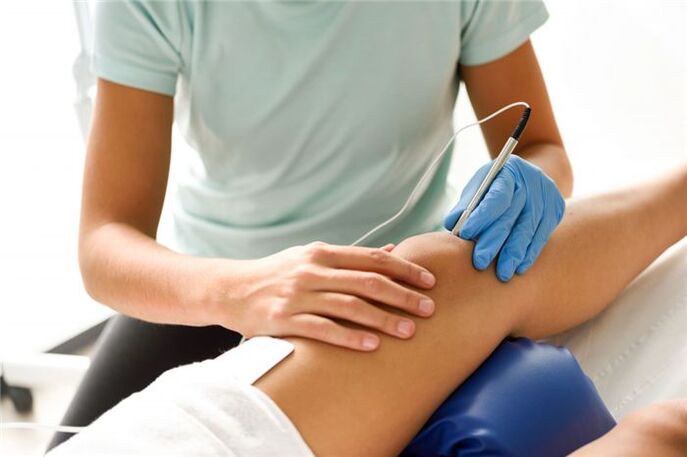
Physiotherapy
Among other physiotherapeutic methods for the treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, the following are used:
- laser and magnetotherapy;
- microwave therapy;
- shock wave therapy;
- breadth;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electrophoresis with analgin, novocaine, chymotrypsin, etc. ;
- phonophoresis with glucocorticoids;
- paraffin and ozokerite applications;
- cryotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- joint traction and kinesitherapy;
- balneotherapy.
Massage to deform osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Therapeutic and lymphatic drainage massage for deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint, as well as manual therapy, are performed by a specialist after the inflammation of the joint has been relieved. For self-massage at home, caresses and rubbing are recommended, as well as movements aimed at stretching muscles and ligaments, a deep warm-up (performed last, after a warming effect). Self-massage goes well with local irritants and essential oils. Remember that with deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint, massage is performed on both joints, even if only one of them is affected.
Exercises to deform osteoarthritis of the knee joints
Therapeutic gymnastics (physical therapy) to deform arthrosis of the knee joint is performed in a sitting or lying position, water aerobics is also effective. An instructor compiles an individual set of exercises to deform osteoarthritis of the knee joint. Below we propose a short warm-up aimed at strengthening the leg muscles.
- Sit on the floor, legs straight, emphasis on the hands behind the back. Bend and straighten your toes.
- The starting position is the same, slowly bend the leg, at the end of the movement rest the toe of the foot on the ground. Repeat with the foot behind the other foot.
- Continue in the same starting position, lift the leg straight in front of you, point towards you.
- Without changing the starting position, we pull our hands on the tips of the straight legs.
- Sitting on the floor, he hugs his bent knee and tries to lift the other leg above the floor.
- Sitting on the floor, spread your legs shoulder-width apart. Rotate your legs in turn so that the toe moves 180 degrees.
- Sitting on the ground, legs bent. Rotate the foot from heel to toe, feeling the work in the back of the thighs.
Excellent! Do exercises to deform osteoarthritis of the knee joint at least 3-6 times a day.
Medicines to deform osteoarthritis of the knee
Drug treatment of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint allows you to quickly stop acute pain, reduce inflammation and swelling, and improve nutrition in the joint. Therefore, drugs are used at all stages of the disease and help restore knee mobility.
Chondroprotectors
Chondroprotectors in the form of tablets, capsules, sachets and injections are used to regenerate and maintain synovial cartilage.
Anti-inflammatory
Steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint. They are prescribed in the form of tablets, injections, sachets, creams, ointments and other products for external and internal use.
Anti-inflammatory drugs can be used in combination with anesthetics, which are injected into the joint cavity as a block.
Antispasmodics
Removal of the spasm is necessary to return the patient to normal activities and the normal supply of nutrients to the tissues.
Angioprotectors
To deform arthrosis of the knee joint, preparations based on horse chestnut and others are used.
Heating agents
Among the warming agents, it is worth highlighting preparations based on natural ingredients: snake and bee venom, red pepper, mustard.
All of these drugs improve the blood supply to the tissues and distract from pain.
Nutrition to deform osteoarthritis of the knee
A healthy diet for deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint includes dishes with a reduced content of trans fats and "fast" carbohydrates. Preference should be given to lean meat and fish, seafood and vegetables, steamed, baked or stewed under a lid. Also useful are fruits, berries and drinks rich in antioxidants: wild plants, blueberries, cranberries, cranberries, green tea and high-quality coffee. You can also eat whole grains, legumes.
But potatoes, white bread, pastries, convenience foods, fast food and alcohol should be excluded.
If you are overweight with deforming knee osteoarthritis, consider low carb diet options.